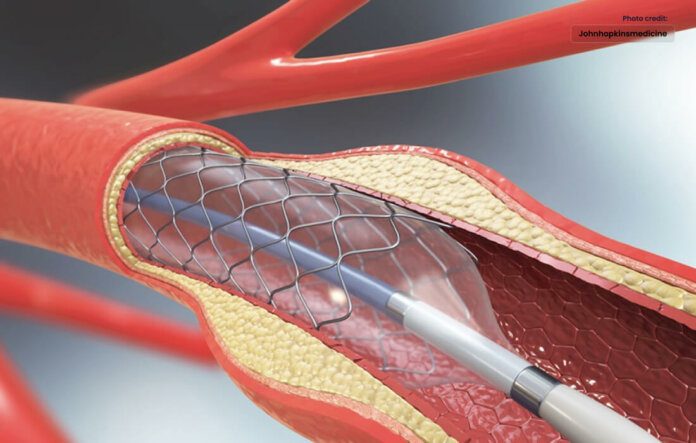
Angioplasties are a non-surgical method of treating clogged arteries.
Introduction:
Cardiovascular diseases continue to be a leading cause of mortality worldwide. Among the various treatment options available, angioplasty has emerge as a significant breakthrough in cardiac care. This minimally invasive procedure has revolutionize the way we treat blockages in the heart’s arteries, offering patients a new lease on life. further, we will explore the intricacies of angioplasty, its benefits, and the path to a healthier heart.
Understanding Angioplasty:
Angioplasty, also known as percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI), is a procedure use to treat coronary artery disease (CAD). It involves the use of a catheter to access the block or narrow arteries in the heart and restore blood flow. The catheter is guide through the blood vessels to the affect area, where a small balloon is inflate to widen the narrowed . In some cases, a stent—a small mesh tube—is also insert to keep the artery open.
Advantages of Angioplasty:
a. Minimally Invasive:
Unlike traditional open-heart surgeries, angioplasty is a minimally invasive procedure that requires only a small incision. This approach significantly reduces the risks associated with surgery, such as infection, bleeding, and a lengthy recovery period.
b. Faster Recovery:
Angioplasty allows for a quicker recovery compared to open-heart surgery. Most patients can be discharged within a day or two after the procedure and resume their normal activities within a few days or weeks, depending on their condition.
c. Restore Blood Flow:
By opening up the blocked or narrowed arteries, angioplasty restores blood flow to the heart muscle. This improves symptoms such as chest pain (angina) and shortness of breath, while also reducing the risk of complications like heart attacks.
d. Increase Longevity:
Angioplasty has shown to improve long-term survival rates in patients with coronary artery disease. By addressing blockages and improving blood flow, the procedure reduces the risk of future cardiac events, thereby increasing life expectancy.
Preparation and Procedure:
Before undergoing angioplasty, patients will undergo various tests and evaluations to determine the extent of the blockages and the overall condition of their heart. This includes electrocardiograms (ECGs), stress tests, and angiograms. Based on the results, the cardiologist will determine if angioplasty is the appropriate treatment option.
During the procedure, the patient is typically awake but under mild sedation. The cardiologist makes a small incision in the groin or wrist area and inserts a thin catheter into the artery. The catheter is guided to the blocked artery, where the balloon is inflated to widen the artery and improve blood flow. In some cases, a stent is inserted to help keep the artery open.
Recovery and Aftercare:
After the angioplasty procedure, patients are usually monitored for a short period to ensure stability. Most individuals can return home within 24 hours. It is essential to follow the prescribed medications, maintain a heart-healthy lifestyle, and attend regular follow-up appointments with the cardiologist. This includes taking medications to prevent blood clotting, adopting a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, managing stress, and avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Potential Risks and Complications:
While angioplasty is considered a safe procedure, there are some risks involved, such as bleeding, infection, allergic reactions to medications or contrast dye, damage to blood vessels, or kidney problems due to contrast dye. However, serious complications are relatively rare, and the benefits of the procedure generally outweigh the risks.
Conclusion:
Angioplasty has revolutionized the treatment of coronary artery disease, offering patients a minimally invasive option with significant benefits. By restoring blood flow and reducing blockages in the heart’s arteries, angioplasty helps improve symptoms, enhance long-term survival rates, and provide patients with a renewed sense of well-being. If you or a loved one is diagnosed with coronary artery disease, consult with a cardiologist to explore whether angioplasty is a suitable treatment option for restoring heart health. Remember, early detection, timely intervention, and adopting a heart-healthy lifestyle are key to preventing and managing cardiovascular diseases.
Find out more about https://rockedgeurdu.com/