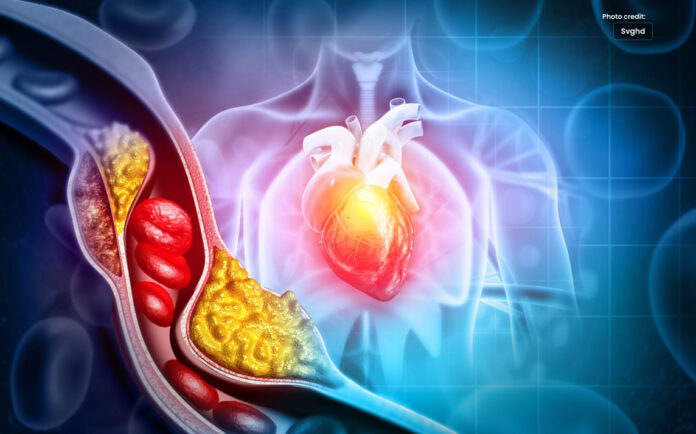
High cholesterol & narrowed arteries increase the risk of blood clots.
Cholesterol test, a component of your annual physical, is important in determining heart health. Heart attacks & blood stokes are linked to high cholesterol.
Especially from certain levels of cholesterol in the blood such as LDL. According to data from the World Health Organization 32% of all deaths worldwide in 2019 were caused by cardiovascular disease.
Most people are unaware that the main cause of heart attacks and strokes is often thrombosis.
Which is the medical term for the formation of blood clots.
According to the Cleveland Clinic, a blood clot is a partially solidified collection of blood that can form in your veins or arteries and block blood flow to that area.
This can result in pulmonary embolism, deep vein thrombosis, heart attack, or stroke.
High cholesterol causes blood clots
High cholesterol levels are linked to blood clot formation in a couple of ways.
Main risk factors for atherosclerosis, the accumulation of fatty plaques on and inside the artery walls, is high levels of a particular type of cholesterol.
The American Heart Association (AHA) states that plaque is composed of lipids, cholesterol, waste products from your cells, fibrin (which causes blood clotting), and calcium.
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), plaque is made up of cholesterol, fats, your cells’ waste products, calcium, and fibrin (which causes blood clotting).
Fatty plaques can restrict the arteries and reduce the amount of blood that reaches your essential organs.
This may result in symptoms like angina, which is characterized by a decreased blood supply to the heart and is frequently felt as chest discomfort when exerting oneself.
Decreased blood supply to the legs can lead to leg pain during exercise, a condition known as intermittent claudication.
According to the Mayo Clinic, the condition is usually a symptom of peripheral artery disease, a narrowing of the arteries in the limbs.
Given the link between high cholesterol and blood clots, the risk is that if one of these plaques ruptures. When you have high cholesterol, those cholesterol particles get stuck in the artery walls.
that cause damage, says Nida Shaban, MD, a cardiologist at Rush University Medical Center.
The artery walls may bulge out due to plaque formation, weakening the walls in the process. although blood clot formation is linked to elevated levels of some cholesterol.
That root cause may be chronic inflammation (from unhealthy lifestyle factors and behaviors around diet, inactivity, stress, etc
A heart attack is caused by blockage of the heart arteries, while a stroke is caused by blockage of the brain arteries.
How can you reduce the risk of blood clots?
Maintaining heart health requires controlling your cholesterol. Regular screening for cholesterol is the first step.
According to Dr. Shaban, all adults should be aware of their cholesterol readings and what they mean in terms of their overall cardiovascular risks.
Your doctor may frequently advise lifestyle modifications, such diet and exercise, if your cholesterol is high in order to lower your blood pressure and lessen systemic inflammation.
Also Read this
Facts About Blood and Blood Donate
Additionally, they might suggest cholesterol-lowering medication, which can help prevent VTE and subsequently a heart attack or stroke.
Dr. Shaban states that, if you do have high cholesterol, you should also be very vigilant about other risk factors in your life.
Additional controllable risk variables that are closely associated with community and lifestyle choices and behaviors include:
- Hypertension
- Smoking
- Diabetes
- Obesity