Blood transfusions, generally safe, have risk requiring practitioners.
This activity reviews the indications for blood transfusions, including for unique client populations, the pre-transfusion planning, and the prospective complications of blood transfusions. In inclusion, this activity highlights the role of the group that is interprofessional in taking care of patients undergoing blood transfusions.
Medicine made developed this is certainly considerable understanding of blood circulation in the past few centuries. For millennia medicine thought in the “four senses of humor” and utilized bloodletting being a treatment.
In the 1600s, William Harvey demonstrated the way the circulatory system functioned. Right after that, boffins became enthusiastic about transfusion, initially transfusing the bloodstream this is certainly animal humans.
Dr. Philip Syng Physick performed the first blood this is certainly individual in 1795, additionally the first transfusion of real human blood for the treatment of hemorrhage took place in England in 1818 by Dr. James Blundell.
Rapid advances were made in understanding blood typing, bloodstream components, and storage space since the 1900s being early. It has progressed into the field of transfusion medicine.
Transfusion medicine involves laboratory and medication that is clinical and physicians from multiple specialties, such as pathology, hematology, anesthesia, and pediatrics, subscribe to the area. Transfusion of red bloodstream cells has turned into a treatment this is certainly fairly common.
Within the United States, around 15 million devices are transfused yearly, while about 85 million devices are transfused global.
Blood Transfusions (FPP)
Blood is usually kept in components. Fresh bloodstream that is whole for ages been looked at as the standard for transfusion; however, health advancement features allowed the efficient use of the various components, such as packed purple bloodstream cells (PRBCs), individual aspect focuses, fresh frozen plasma (FFP), platelet focuses, and cryoprecipitate.
Consequently, current indications for entire blood transfusions are usually few. The US buddy is certainly a military system and is the most extensive system of entire blood transfusion.
Furthermore, entire blood transfusions in civil pre-hospital configurations plus the injury bay is seeing a resurgence in some areas. The hemoglobin in purple blood cells binds air and it is your body’s main way to obtain oxygen delivery. A single unit of loaded bloodstream this is certainly red is roughly 350 mL and contains about 250 mg of metal.
Tips on red bloodstream mobile transfusion from the American Association of Blood Financial Institutions advise a strategy this is certainly limiting stable patients with non-hemorrhaging anemia.
While there may be variants, anemia is usually thought of as a hemoglobin amount of not as much as 13 g/dL in males and less than 12 g/dL in females. While presently, a more threshold is certainly restrictively used to determine the sign of transfusion, formerly, a liberal method, usually choosing a cutoff of hemoglobin significantly less than 10 g/dL, ended up being used, regardless of symptoms.
Blood Transfucions (RBC)
Currently, instructions for the transfusion of Red Blood Cells (RBC) usually follow a threshold this is certainly limiting. Because there is some difference within the quantity for the limit, 7 g/dL is definitely an agreed-upon worth for asymptomatic customers being healthy.
Several research indicates this is a limit this is certainly acceptable to other client communities, including those with gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding and critically sick patients.
The rules recommend a value of 8 g/dL because of the threshold in clients with coronary artery conditions or those undergoing surgeries which are orthopedic. Nonetheless, this can be added to the lack of literature on using a threshold of 7 g/dL within the assessment research of the communities which can be diligent.
The guidelines and clinical studies on transfusion requirements in important attention (TRICC) additionally recommend a value of 7 g/dl as the limit for critical customers that are sick.
Transfusion can also be indicated in patients with active bleeding that is intense customers with signs linked to anemia (for instance, tachycardia, weakness, dyspnea on effort) and hemoglobin less than 8 g/dL.
Blood Transfucions ‘Anemia’
Anemia, in such cases, is described as a decreased circulating cell that is red, thought of as grams of hemoglobin per 100 ml of the entire bloodstream. Anemia may possibly occur because of loss this is certainly exterior inadequate production, interior destruction, or perhaps a mixture of these elements.
Even though many customers experiencing hemorrhaging this is certainly active anemic, anemia by itself will not be an indication for transfusion. Caused by serious hemorrhage is a state of shock, and surprise is the inadequate availability of oxygen to undertake metabolic rate this is certainly mobile.
Red mobile mass repletion is one element of the management of hemorrhagic shock.
Unless the patient is definitely bleeding, it is recommended to transfuse 1 product of packed cells which are red a period, which will typically raise the hemoglobin value by 1 g/dL and hematocrit by 3%.
Follow through by examining post-transfusion Hemoglobin
The American Society of Anesthesiologists recommends transfusion at hemoglobin quantities of 6 g/dL or less. However, more data can be recent diminished mortality with pre-anesthetic hemoglobin of more than 8 g/dL, particularly in renal transplant patients.
The transfusion of fresh frozen plasma (FFP) is typical, but there are restricted indications that are certain of its usage. There is evidence this is certainly insufficient for its use within numerous clinical scenarios, such as prophylaxis in nonbleeding patients.
FFP transfusion might be suggested in hemorrhaging clients to replace lost coagulation facets. Clinical circumstances satisfying this criterion feature cardiopulmonary bypass, massive transfusion, decompensated liver disease, extracorporeal pulmonary support practices, or intense disseminated coagulation that is intravascular.
In past times, FFP, coupled with vitamin K, ended up being indicated for warfarin excess in cases of life-threatening hemorrhage. FFP is rarely required in supplementing K warfarin or deficiency reversal because prothrombin complex concentrate is widely accessible. The exception is in the complete cases of concomitant plasma volume deficit.
Platelet transfusion is helpful in instances of platelet dysfunction or deficiency. In customers with bone marrow failure, prophylactic platelet transfusion is suggested whenever there are no other risk facets for bleeding and platelet matters are below 10 X 10/L.
If other connected risk facets exist, the threshold to transfuse could be raised to 20 X 10/L. A prerequisite to processes that are unpleasant is platelet counts greater than 50 X 10/L.
In the complete case of active hemorrhage, platelet transfusion ought to be done when thrombocytopenia contributes towards the hemorrhage, additionally, the platelets are significantly less than 50 X 10/L. If you have diffuse bleeding that is microvascular the platelets must certainly be maintained above 100 X 10/L.
Contraindications
There are no contraindications that are absolute many clients or their customers (in pediatric cases) may not get transfusions on spiritual grounds.
Whole bloodstream transfusion is certainly not suggested when treatment that is component-specific readily available, such as for example utilizing purple blood cells to treat anemia or utilizing fresh frozen plasma to take care of coagulopathy.
Entire bloodstream transfusion can lead to problems being numerous for instance, volume overload, and that’s why you should utilize component therapy whenever feasible.
Equipment
Blood products are transfused through intravenous tubing with filters. The filters, which typically have pore diameters of 170 to 260 microns, may also be made use of to prevent particulate debris from being administered.
Nonetheless, the particulate that is trapped in bacterial growth, plus the American Association of Blood Banks (AABB) recommends against getting a filter for longer than four hours. Before transfusion, the tubing must certainly be primed by having an isotonic, calcium-free blood-compatible option, for example, typical saline.
Citrate is used as a preservative in loaded blood this is certainly purple, and clots will develop in the intravenous range if you have more calcium compared to citrate can buffer.
The following is a list of suggested supplies needed for a blood transfusion:
Through various central venous access devices or peripheral intravenous catheters, blood components or entire blood may be given. It’s important to think about the following sizes:
- 20-22 gauge for routine transfusion in adults
- 16-18 gauge for rapid transfusion in adults
- 22-25 gauge for pediatrics
- The requirements for administration sets might vary
- Blood filters
- The administration of platelet-poor plasmas requires supplies that often differ by product and brand.
- Infusion devices, such as infusion pumps, blood warmers, rapid infusers, and pressure devices, can be used to transfuse blood components.
- A pressure infusion device may be needed for the rapid transfusion of blood components.
- A blood warmer device is often needed to prevent hypothermia in the rapid administration of cold-blood components, for instance, in trauma settings or operation theatres.
Personnel
Two providers should validate bloodstream items before administering, and patients should be administered during transfusion by qualified employees. Bloodstream transfusions can be executed by various health providers, such as subscribed nurses, accredited vocational nurses, or licensed nurses that are practical.
Nurses usually perform this task under the guidance of a physician. Regarding bloodstream transfusion education demands, most professionals, such as registered nurses, and accredited vocational nurses, learn how to carry bloodstream transfusions through medical education and programs that are educational.
Preparation
Planning for bloodstream transfusion requires pretransfusion this is certainly running for compatibility between person antibodies and donor red blood cells. This involves receiving a test regarding the recipient’s bloodstream to deliver for the display and kind.
The nature and screen test verifies the recipient’s blood type and also determines in the event that the recipient features any” that is“unexpected-ABO) antibodies which may create a response. You will find multiple options for running this display.
In the event that the display is bad, it’s very unlikely you will see a response. Getting the bloodstream when it comes to the patient should rapidly be done if required. If the display screen is good, many bloodstream banking institutions will crossmatch and hold two units of bloodstream for the patient in the event they require a transfusion.
Another prerequisite to blood transfusion is always to simply take permission from the client when possible.
The list of crucial actions to take before beginning a blood transfusion is as follows:
Find the Current Type and Crossmatch
- Take a blood sample, which lasts up to 72 hours
- Send the sample to the blood bank
- Ensure that the blood sample has the correct labeling with the date and timing
- Wait for the blood bank to crossmatch and prepare the needed units
Obtain Informed Consent and Health History
- Discuss the procedure with the patient
- Confirm the past medical history and any allergies
- The supervising provider should have obtained signed consent from the patient
Obtain Large-bore Intravenous Access
- This is 18 gauge or larger IV access
- Each unit should be transfused within 2-4 hours
- A second IV access should be secured in case the patient needs additional IV medications
- Normal saline is the only fluid that can be administered with blood products
Assemble Supplies
- Y tubing with an in-line filter
- 0.9% NaCl solution
- Blood warmer
Obtain Baseline Vital Signs
- These include heart rate, temperature, blood pressure, pulse oximeter, and respiratory rate
- Respiratory sounds and urine output should also be documented
- Notify the provider if the temperature is more than 100 F
Obtain Blood from the Blood Bank
- Once the blood bank notifies that the blood is ready, its delivery from the blood bank should be ensured
- Packed red blood cells can only be given one unit at a time
- Once the blood has been released for the patient, there are 20-30 minutes to begin the transfusion and up to four hours to complete it.
Technique or Treatment
Here are some general procedures medical professionals should adhere to when performing a blood transfusion:
- Verify Blood Product
- Relay the features of a transfusion reaction to the patient. The patient should inform the nursing staff during the transfusion if these appear.
- Baseline vital signs, lung sounds, urine output, and skin color
- Prepare the Y tubing with 0.9% NaCl and have the blood unit ready in an infusion pump
- The blood should be run slowly for the first fifteen minutes, for instance, 2 ml/min or 120 ml/hr
- Staff should be supervising the patient for the first fifteen minutes as this is when most transfusion reactions happen
- The rate of transfusion can be increased after this period if the patient is stable and does not display any signs of a transfusion reaction
- Document vital signs after fifteen minutes, then every hour, and finally, at the end of the transfusion
- During the transfusion, look for any signs of transfusion reactions
- If a reaction is suspected, stop the transfusion immediately
- Disconnect the blood tubing from the patient
- Inform the provider, stay with the patient, and assess the status
- Document everything
- After the transfusion, flush the Y tubing with normal saline and dispose of the used Y tubing in the biohazard bin
- Obtain post-transfusion vital signs
- After the procedure, some patients could experience soreness at the puncture site, but this should dissipate quickly.
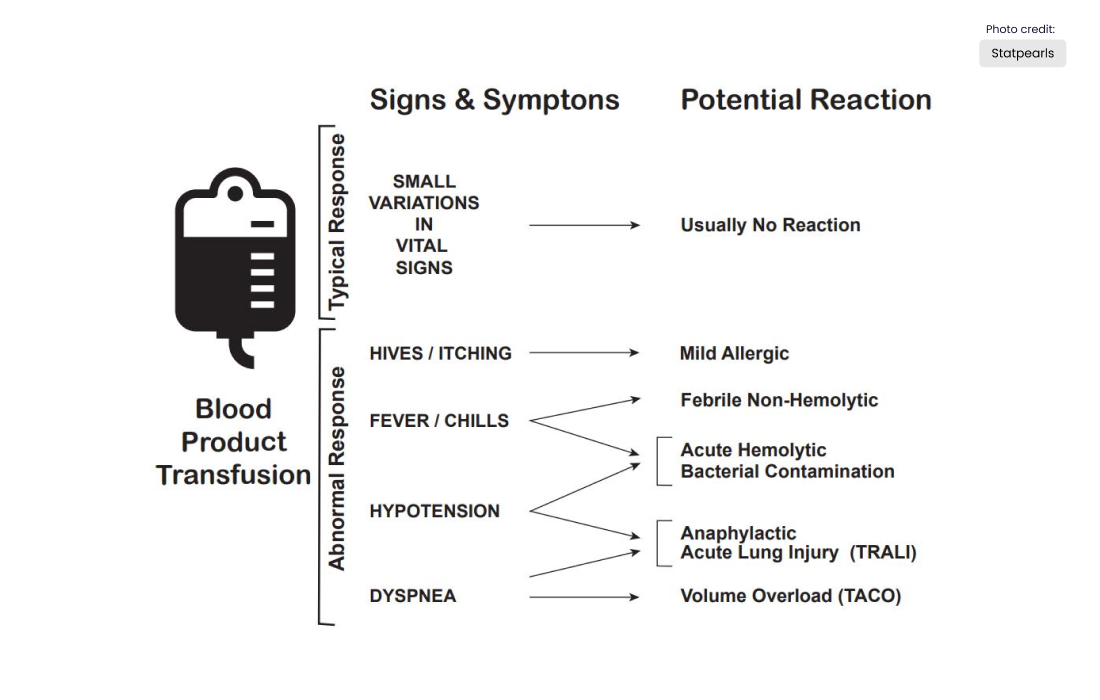
Complications
There are multiple complications of blood transfusions, including infections, hemolytic reactions, allergy symptoms, transfusion-related lung injury (TRALI), transfusion-associated circulatory overburden, and instability that is an electrolyte.
Based on the American Association of Bloodstream Banks (AABB), febrile reactions will be the most common, followed by transfusion-associated circulatory overload, allergic reaction, TRALI, hepatitis C viral disease, hepatitis B viral infection, personal immunodeficiency virus (HIV) illness, and deadly hemolysis that will be acutely uncommon, only happening virtually 1 in 2 million transfused products of RBC.
For comparison, the lifetime likelihood of dying from a lightning hit is about 1 in 161,000.
A list of approximate danger per unit transfusion of RBC (adapted from AABB tips that are clinical JAMA November 15, 2016) would be talked about right here.
Adverse Event and Approximate Risk Per Unit Transfusion of RBC
- Febrile reaction: 1:60
- Transfusion-associated circulatory overload: 1:100
- Allergic reaction: 1:250
- TRAIL: 1:12,000
- Hepatitis C infection: 1:1,149,000
- Human immunodeficiency virus infection: 1:1,467,000
- Fatal hemolysis: 1:1,972,000
Febrile Reactions
Transfusing with leukocyte-reduced bloodstream products, which most blood products when you look at the United States are, may reduce reactions being febrile. If this does occur, the transfusion is halted, in addition to the client examined, as a hemolytic reaction can at first appear similar, and consider performing a hemolytic or workup that is infectious.
The therapy is by using acetaminophen and, if needed, diphenhydramine for symptomatic control. The transfusion is started again at a slower rate after treatment and the exclusion of other causes.
Transfusion-associated Circulatory Overload
It really is seen as respiratory distress in addition to cardiogenic edema that is pulmonary. This reaction is common in customers currently in a fluid-overloaded state, such as congestive heart failure or intense failure this is certainly renal.
Diagnosis is based on symptom onset within 6 to 12 hours of finding a transfusion, clinical evidence of fluid overload, pulmonary edema, elevated brain natriuretic peptide, and reaction to diuretics.
Preventive attempts and therapy include restricting the number of transfusions to the amount that is most affordable and required, transfusing at the slowest possible time, and administering diuretics before or between transfusions.
Allergic Reaction
It often exhibits urticaria and pruritis and occurs within just 1% of transfusions. More symptoms that are severe such as bronchospasm, wheezing, and anaphylaxis, tend to be unusual. Allergic responses might be present in patients who’re IgA lacking, as contact with IgA in donor items may cause an anaphylactoid effect this is certainly serious.
This is often precluded by washing the plasma from the cells ahead of transfusion. Mild signs, such as for example urticaria and pruritis can usually be treated with antihistamines. Much more symptoms which are severe be treated with bronchodilators, steroids, and epinephrine.
TRALI: transfusion-related lung injury
This really is uncommon, occurring in about 1:12,000 transfusions. Clients will develop symptoms within 2 to 4 hours after finding a transfusion. Clients will build up intense respiratory that is hypoxemic, similar to intense breathing stress syndrome (ARDS).
Customers will have edema that is pulmonary regular CVP, without evidence of remaining heart failure CVP. Diagnosis is made according to a history of present transfusion, chest x-ray with diffuse infiltrates that are patchy, and the exclusion of other etiologies.
The rest of the 90% will resolve within 96 hours with supporting treatment just since there is a 10% death.
Infections
These are possible problems. Hepatitis C and HIV risk, however, are less than 1 in a million due to the screening of potential donors, which has reduced the danger of infections.
A bacterial infection can also happen, but it does so infrequently—roughly once every 250 000 transfusions of red blood cells.
Fatal Hemolysis
This is certainly exceedingly uncommon, occurring just in 1 out of nearly 2 million transfusions. It benefits from ABO incompatibility, plus the recipient’s antibodies recognize hemolysis that induces the donor’s transfused cells.
Clients will build up a beginning this is certainly acute of chills, reasonable back pain, flushing, dyspnea as well as getting tachycardic and entering shock. Treatment is to end the transfusion, leave the IV in position, intravenous fluids with normal saline, and keep urine results greater than 100 mL/hour, diuretics can also be required.
Cardiorespiratory assistance might be offered as appropriate. A workup this is certainly hemolytic also be performed, including giving the donor blood and tubing and post-transfusion labs (see below for record) from the person to the bloodstream lender.
- Retype and crossmatch
- Direct and indirect Coombs tests
- Complete blood count (CBC), creatinine, PT, and PTT (draw from the other arm)
- Peripheral smear
- Haptoglobin, indirect bilirubin, LDH, plasma-free hemoglobin
- Urinalysis for hemoglobin
Electrolyte Abnormalities
Although uncommon and more frequently connected with big-volume transfusions, they can also happen.
- Hypocalcemia can result as citrate, an anticoagulant in blood products, binds with calcium.
- Hyperkalemia can occur from the release of potassium from cells during storage. Higher risk in neonates and patients with renal insufficiency.
- Hypokalemia can result as a result of alkalinization of the blood as citrate is converted to bicarbonate by the liver in patients with normal hepatic function.
Clinical Significance of Blood Transfusions
The research of transfusion medicine, like the transfusion of red bloodstream cells, features evolved significantly over the past century as mentioned in the introduction. The world of transfusion medicine has evolved besides and includes representation from multiple areas being health.
The capacity to transfuse cells being purple clients properly and quickly has actually revolutionized the proper care of upheaval customers, surgical clients, and customers with gastrointestinal bleeding, among other problems.
Transfusion medication will continue to evolve, and research is continuing to boost this technique, in addition to working on alternate ways to carry air to cells, which will possibly reduce steadily the chance of responses and convenience and disease storage.
Improving Healthcare Blood Transfusions Team Results
Our understanding of bloodstream transfusion features enhanced significantly in the last three years. Unlike before, empirical bloodstream transfusions are no longer the norm.
While bloodstream products have an advantage, they are able to also cause damage.
Healthcare workers who take care of customers needing a bloodstream transfusion should consult well a hematologist if they remain not sure in regards to the indications.
Interprofessional team collaboration is vital in handling clients’ bloodstreams that are undergoing and people having adverse reactions to transfusions.
The main element will be lower the damage from unnecessary blood transfusions.
Officially Published by Statpearls